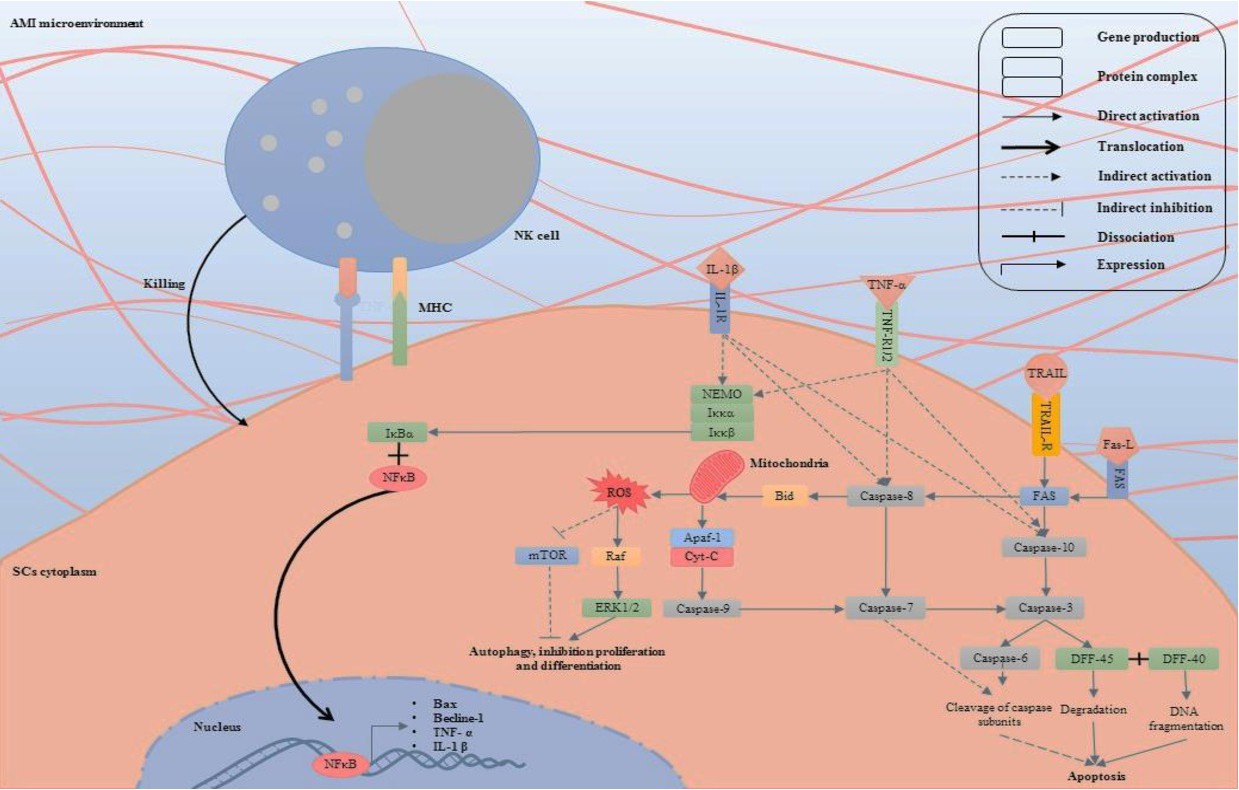
Fig. 3. The SCs interaction with AMI inflammatory microenvironment. TNF-R1/2, IL-1R, Fas, and TRAIL-R as the main death ligands have a central role in inducing SCs death into the inflammatory microenvironment of AMI. During the maintained process, activation of the Fas and the TRAIL-R ligands by their stimulators can directly promote caspase-8 and -10 related apoptosis cascades. In addition, caspase-8 and -10 related cascades indirectly can promote through TNF-α and IL-1β secretion. Following, apoptosis cell death occurs within activation of caspase-7 and then caspase-3. Moreover, activation of Caspase-3 through caspase-6 stimulation and dissociation of DFF-40 and DFF-45 leads to apoptosis in the implanted cells. On the other hand, activation of the mitochondrial related pathways can effectively enhance SCs death. Formation of apoptosome complex (Cyt-C + Apaf-1) through caspase-9 activation, ROS production via activation of MAPK (ERK 1/2) signaling pathway, and inhibiting the mTOR cause to SCs apoptosis, autophagy as well as inhibition of SCs proliferation and differentiation. Furthermore, NF-κB stimulation and translocation into the nucleus by TNF-R1/2 and IL-1R has a central roles in overexpression of pro-apoptotic and also pro-inflammatory cytokine genes. Expression of some MHCs on the implanted SCs into the AMI inflammatory microenvironment via recruitment of NK cell leads to the rejection of the SCs. Abbreviations: AMI: acute myocardial infarction, Apaf-1: apoptotic protease activating factor 1, Bax: Bcl-2-associated X protein, Becline-1: coiled-coil myosin-like BCL2-interacting protein, Bid: BH3-interacting domain death agonist, Cyt-C: cytochrome -C, DFF: DNA fragmentation factor, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinases, Fas: apoptosis antigen 1 (APO-1 or APT), Fas-L: Fas ligand, IL-1R: interleukin-1 receptor, IL-1β: interleukin-1 β , IκBα: nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor-α, Iκκ: inhibitory Kappa Kinase α, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, MHC: major histocompatibility complex, mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin, NEMO: NF-kappa-B essential modulator, NFκB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells , NK cells: natural killer cells, Raf: serine/threonine-protein kinase, ROS: reactive oxygen spices, SCs: stem cells, TNF-R: tumor necrosis factor receptor, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor- α, TRAIL: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, and TRAIL-R: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing receptor., and Becline-1: coiled-coil myosin-like BCL2-interacting protein